Figure 1 from A new time-scale for ray-finned fish evolution
5 (455) In stock

Figure 1. Alternative trees and group names of the major living actinopterygian clades: polypterids (bichir and reedfish); chondrosteans (sturgeons and paddlefish); lepisosteids (garpike); amiids (bowfin); and teleosts. (a) Topology from morphological data, supporting the Neopterygii (Regan 1923; Patterson 1973). (b) ‘Ancient Fish Clade’ topology obtained from mitochondrial genomic data (Inoue et al. 2003; present analysis) and some nuclear genetic data (Venkatesh et al. 2001). a, the Actinopterygii; b, the Actinopteri; g, the Neopterygii; d, the ‘Ancient Fish Clade’. - "A new time-scale for ray-finned fish evolution"
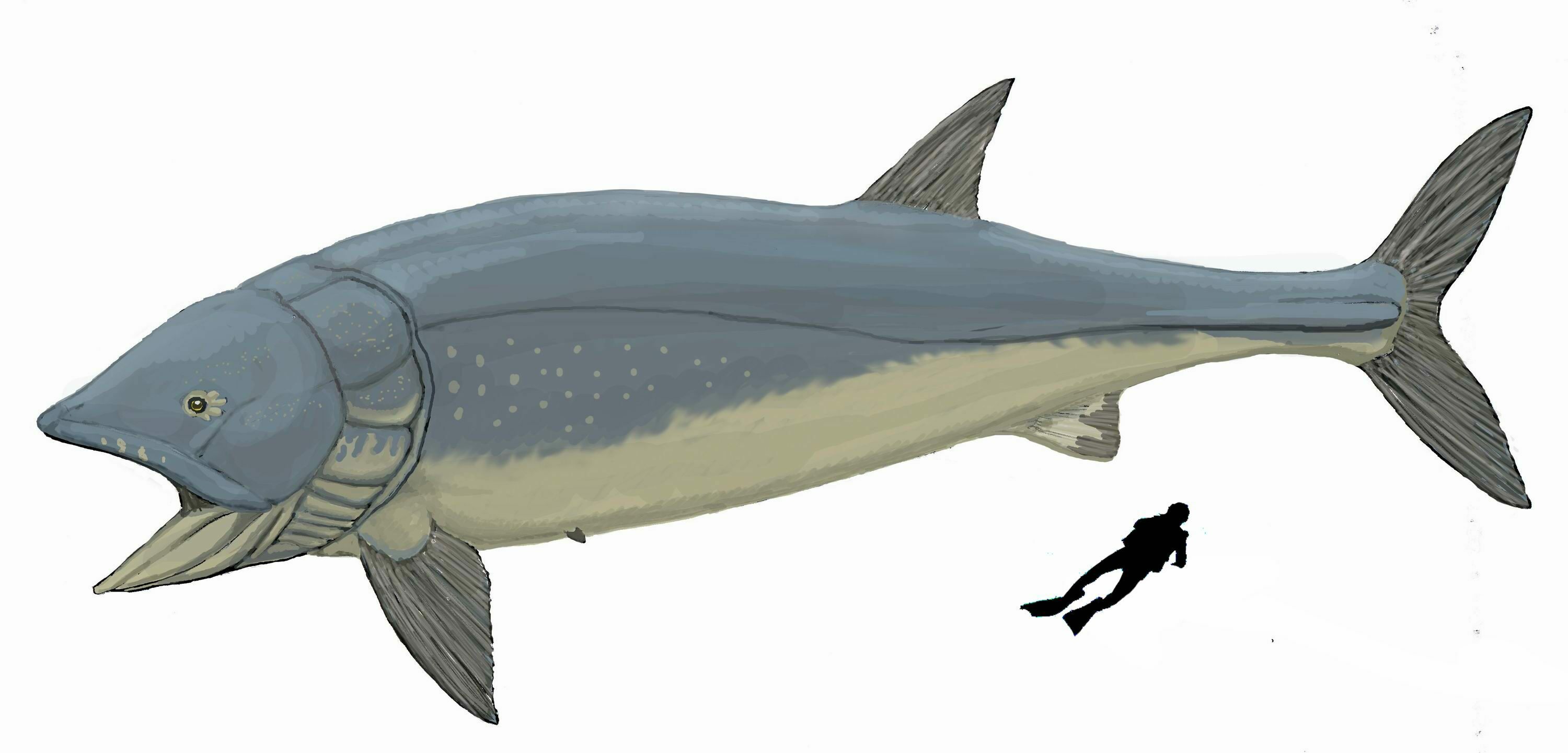
The Evolution Of Fish

Weird 'living fossil' fish lives 100 years, pregnant for 5

Sarcopterygii Archives - Untamed Science

Exceptional fossil preservation and evolution of the ray-finned fish brain

Tiktaalik and the Fishy Story of Walking Fish, Part 2

Coevolution of the olfactory organ and its receptor repertoire in ray-finned fishes

If I could turn back time: an embryological look at the fin-to-limb transition - the Node
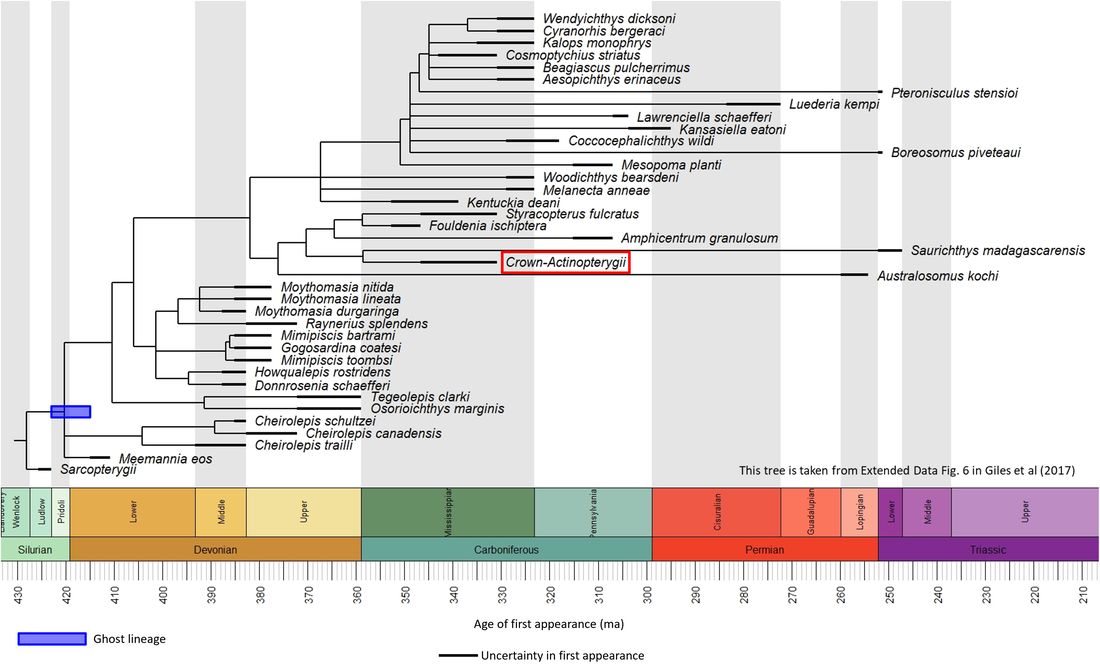
Actinopterygian stem group

The early evolution of ray‐finned fishes - Friedman - 2015 - Palaeontology - Wiley Online Library
Phylogenetic taxonomy of the Vertebrates
1. You might be surprised to learn that the fish sold
The mitochondrial phylogeny of an ancient lineage of ray-finned
Thomas Near on X: Coming soon from Near and Thacker @thackfish
Palaeos Vertebrates Tetrapoda : Amphibians, Systematics, and
 16mm Burn film, Light Leaks, scratches, , Stock Video
16mm Burn film, Light Leaks, scratches, , Stock Video Fox Rage Prism X Travel Heavy Spin 2.40m 30-100g, Fishingtackle24
Fox Rage Prism X Travel Heavy Spin 2.40m 30-100g, Fishingtackle24 Led Luminous Glowing Hair Tie Large Scrunchie Hair Rope Hair - Temu
Led Luminous Glowing Hair Tie Large Scrunchie Hair Rope Hair - Temu Amazing Commercial Fishing Net Catch Giant Tuna - Net Fishing Tuna Catch Hundreds Tons Tuna on Boat
Amazing Commercial Fishing Net Catch Giant Tuna - Net Fishing Tuna Catch Hundreds Tons Tuna on Boat Barracuda Cast Net for the win.
Barracuda Cast Net for the win. Rainbow Stitched Fishtail Paracord Bracelet (Purple) - 5.75 / Purple
Rainbow Stitched Fishtail Paracord Bracelet (Purple) - 5.75 / Purple